Tech Genetics and the Future of Forests
"Digital Frontier," highlighting how cutting-edge technology and genetic science are revolutionising modern forestry
Wednesday, December 17, 2025

The third day of the Tropical Forestry Conclave at KSCSTE-KFRI focused on the "Digital Frontier," highlighting how cutting-edge technology and genetic science are revolutionising modern forestry. Experts gathered to discuss the transition from traditional field-based observations to a high-tech era defined by satellite surveillance, genomic sequencing, and Artificial Intelligence.
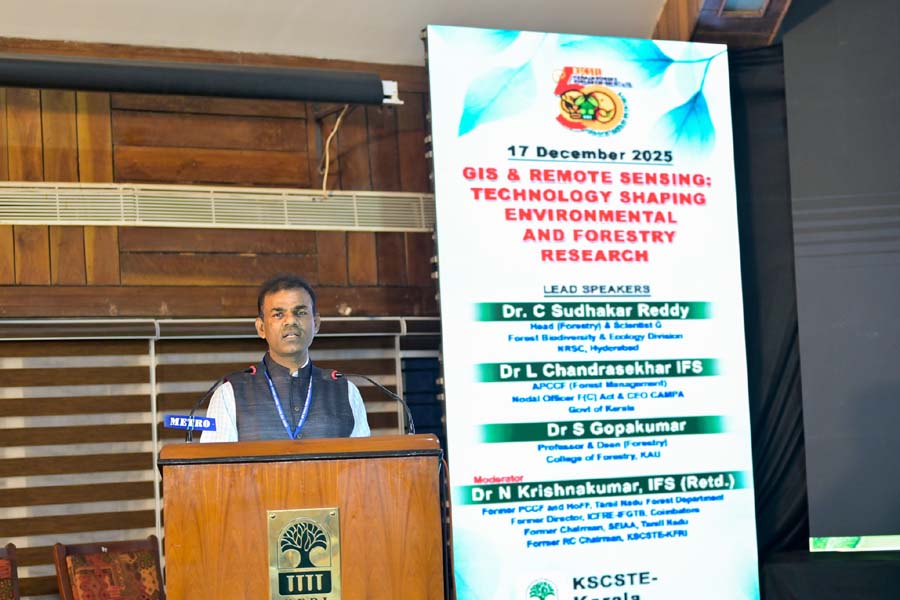
Space-Borne Surveillance and Spatial Data
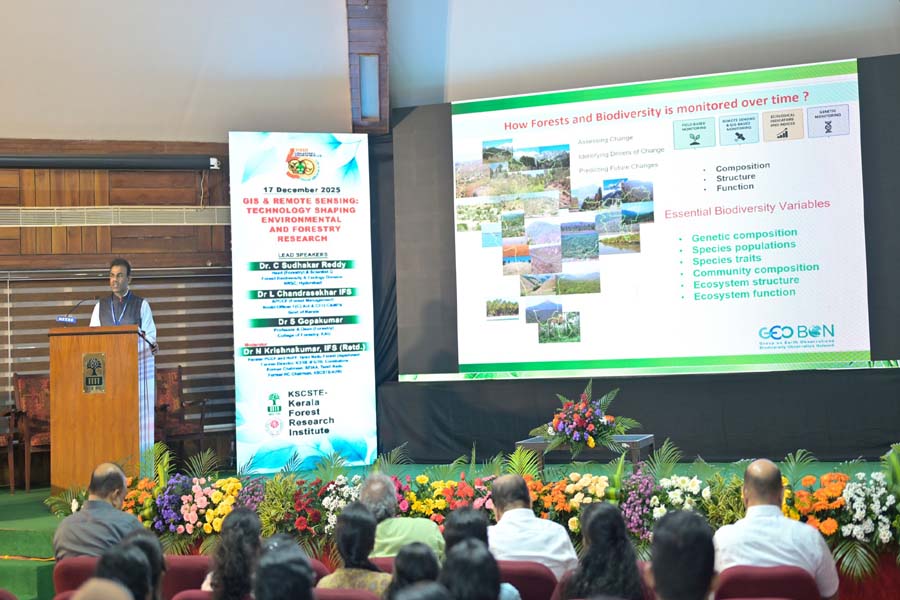
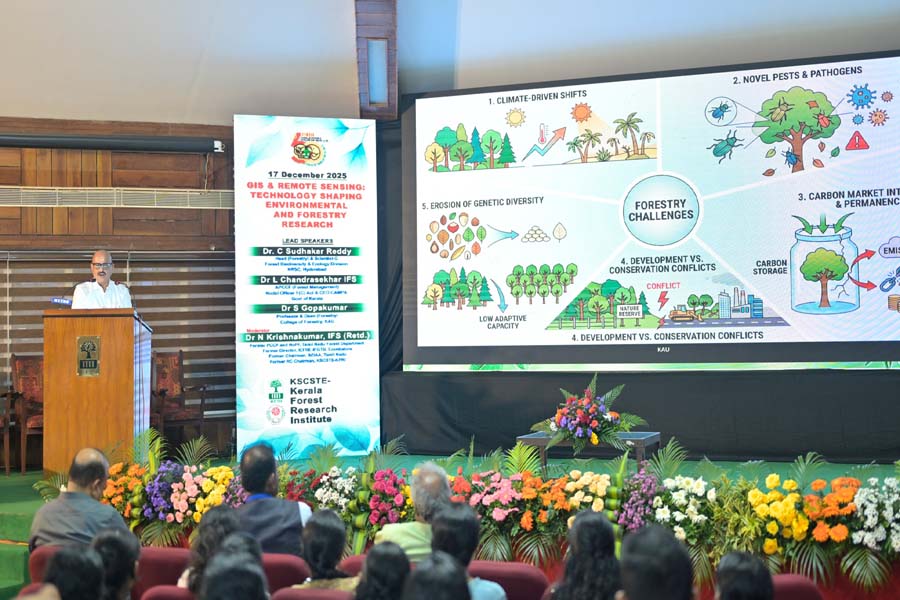
The morning sessions highlighted the critical role of GIS and Remote Sensing. Dr. C. Sudhakar Reddy (NRSC, Hyderabad) and Dr. L. Chandrasekhar IFS discussed how satellite-derived spatial data is no longer just for mapping but is a vital tool for real-time monitoring of forest health and CAMPA (Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority) initiatives. By overlaying layers of topographic, climatic, and vegetation data, foresters can now predict vulnerability to fire and illegal encroachment with unprecedented accuracy.
Unlocking the Genetic Code of Tropical Forests
The conclave took a deep dive into Next-Generation Genomics, exploring how biotechnology can "future-proof" our forests. Scientists from ICFRE-IFGTB, including Dr. Mathish Nambiar Veetil and Dr. Modhumita Dasgupta, presented research on identifying genetic markers for climate resilience and disease resistance in indigenous tree species. This "molecular breeding" approach allows researchers to select the strongest genetic candidates for afforestation, ensuring that the forests of tomorrow can survive the escalating stresses of global warming.
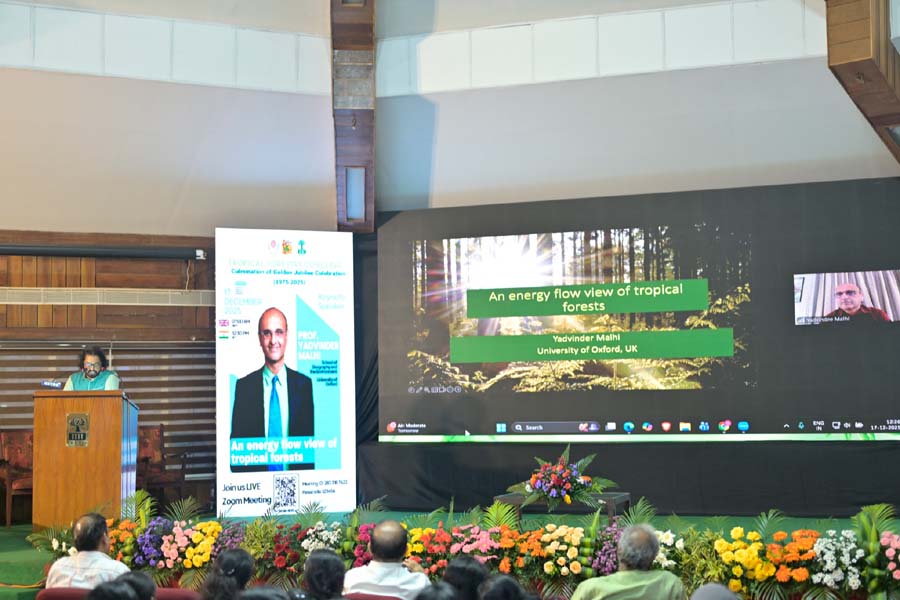
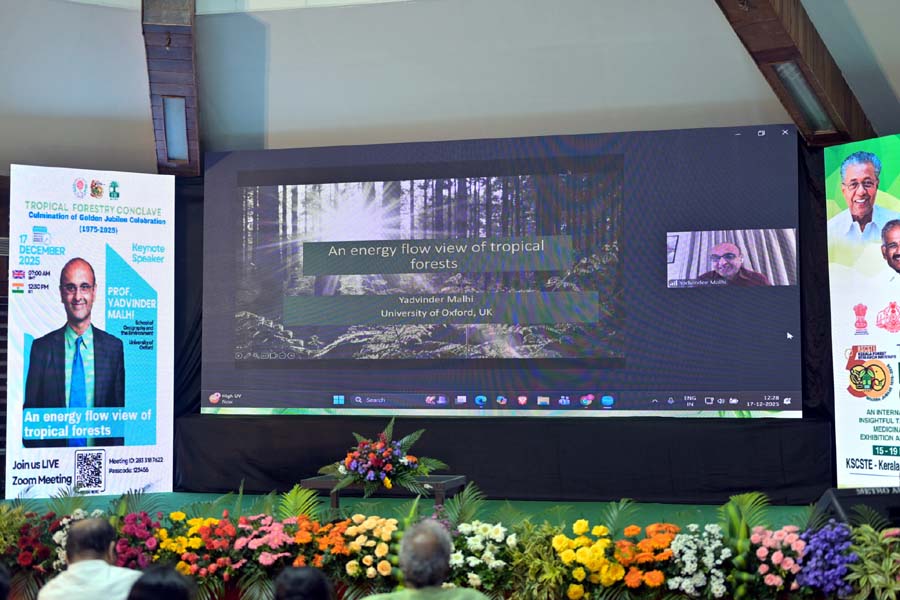
Keynote: Forests as Energy Processors
A major highlight was the special keynote by Prof. Yadvinder Malhi of the University of Oxford. He presented a unique "energy flow view" of tropical forests, reimagining ecosystems not just as collections of trees, but as complex biological machines that capture and transform solar energy. His talk underscored the importance of maintaining ecosystem energetics to ensure the continued provision of services such as carbon sequestration and water regulation.
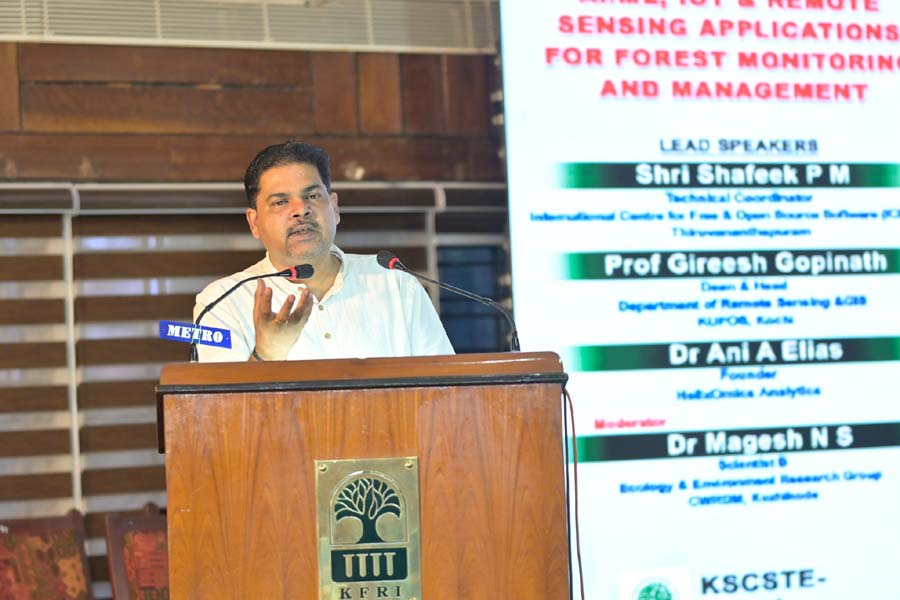
The Rise of "Digital Forests"
The afternoon focused on integrating AI, Machine Learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT). From acoustic sensors that detect the sound of illegal chainsaws to drones that map remote canopies, the "Digital Forests" session showcased how automated systems are reducing the burden on ground personnel. Panelists emphasized that while the tools are digital, the impact is physical—enabling swifter interventions to protect biodiversity.
As the conclave heads into its final days, the focus will shift from the laboratory and the satellite to the marketplace and the community, with upcoming meetings on medicinal plants and stakeholder policy.